Shell of the Week: The Dog-head Triton
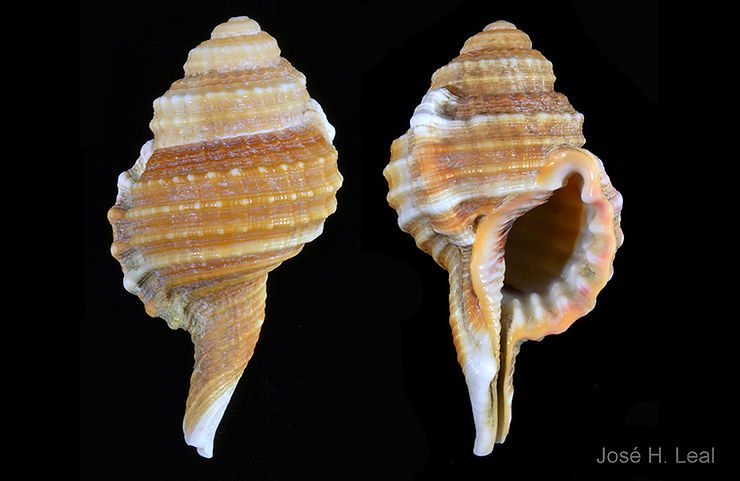
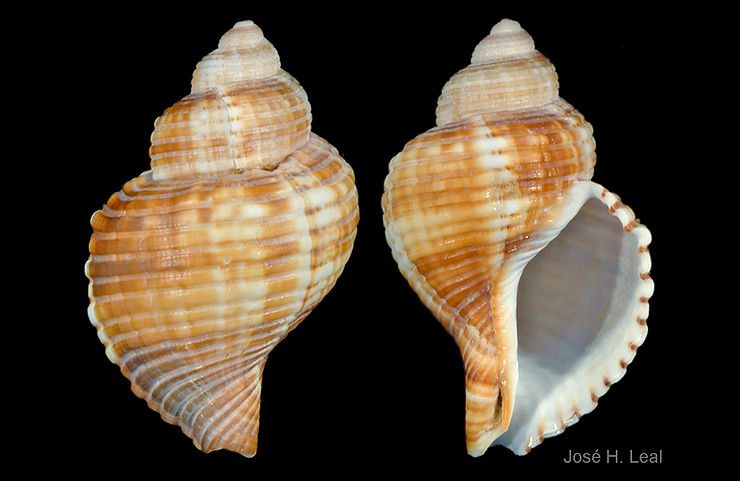
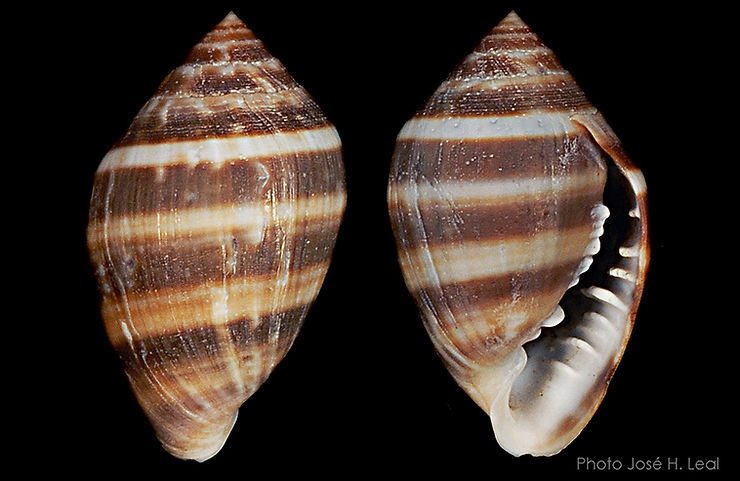
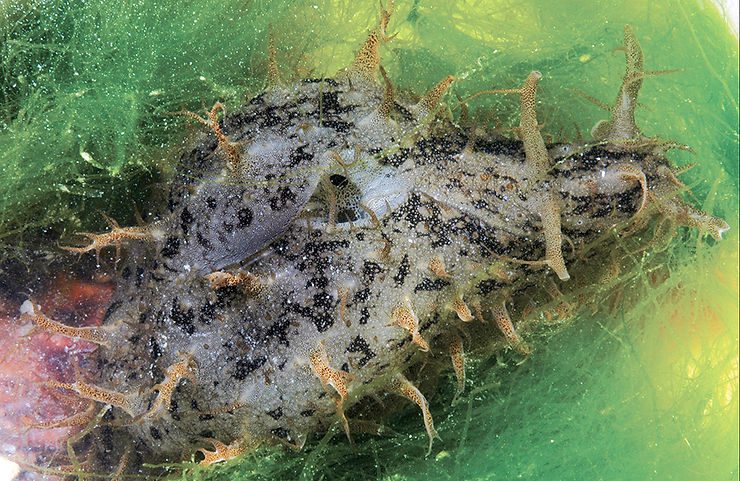
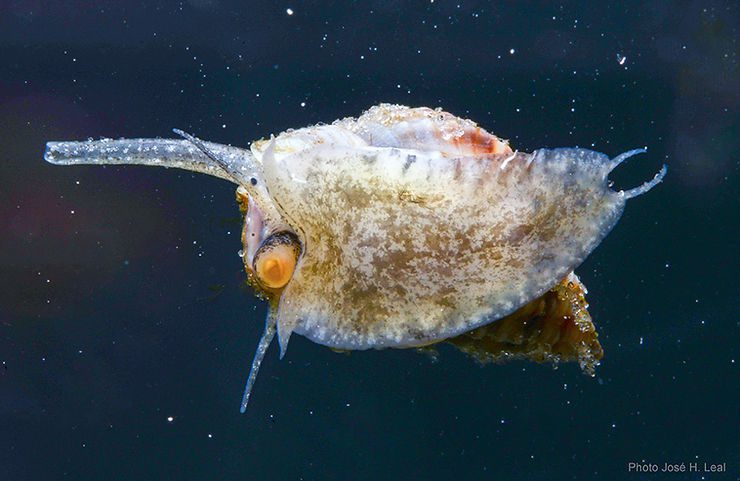
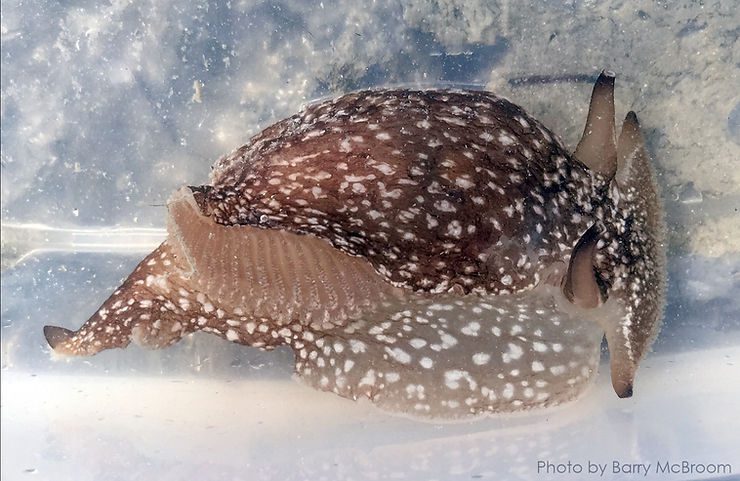
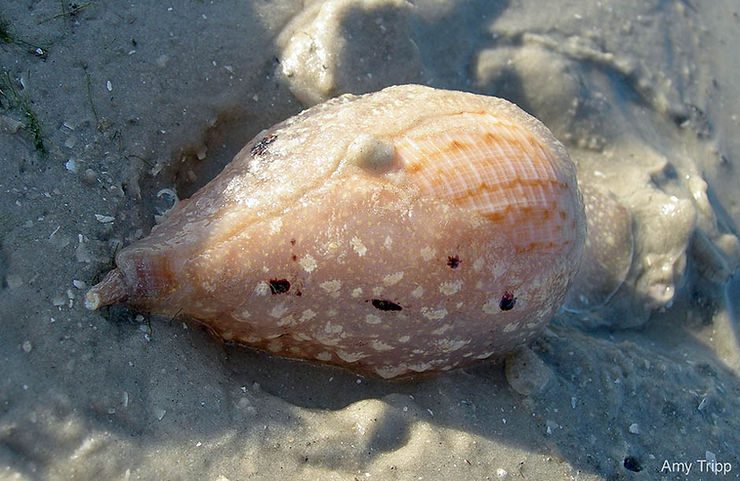
Ranularia cynocephala (Lamarck, 1816) has a sturdy shell that reaches 70 mm (about 2.8 inches). The shell has squarish whorls, a long siphonal canal that may be recurved, and may bear a varix, which denotes the occurrence of a growth stop). The shell sculpture consists of strong spiral cords crossed by weaker axial ribs. The outer lip of the shell aperture is garnished internally with 7 strong, white teeth. The shell color is usually golden-brown, often with a whitish spiral band near the middle