Shell of the Week: The Antillean File Clam
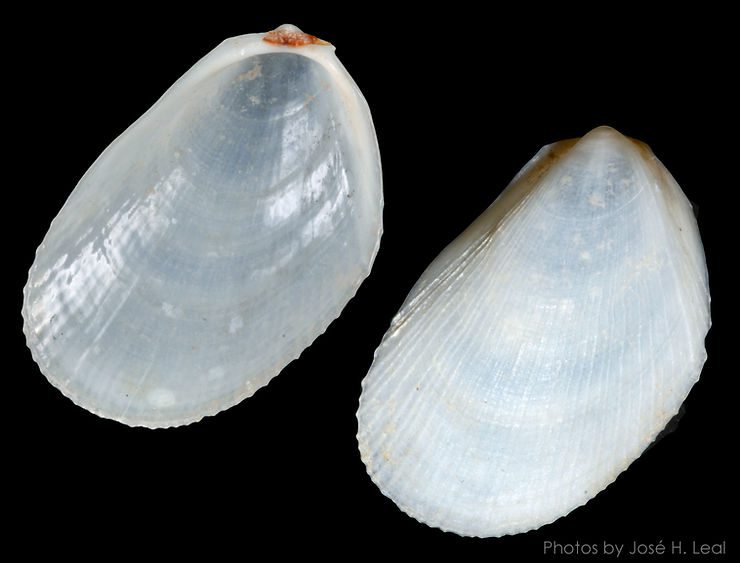
Limaria pellucida (C.B. Adams, 1848) reaches 25 mm (one inch), and has, like most species in the family Limidae, an oval-elongate shell that resembles a “distorted,” or asymmetrical, scallop. The shell is thin-walled, translucent-white, with many narrow radial ribs of irregular width and distribution. The hinge “ears” have about the same size. The clam has salmon-pink gills and relatively large translucent-white tentacles festooned with white “rings” over their entire length. Records of beached